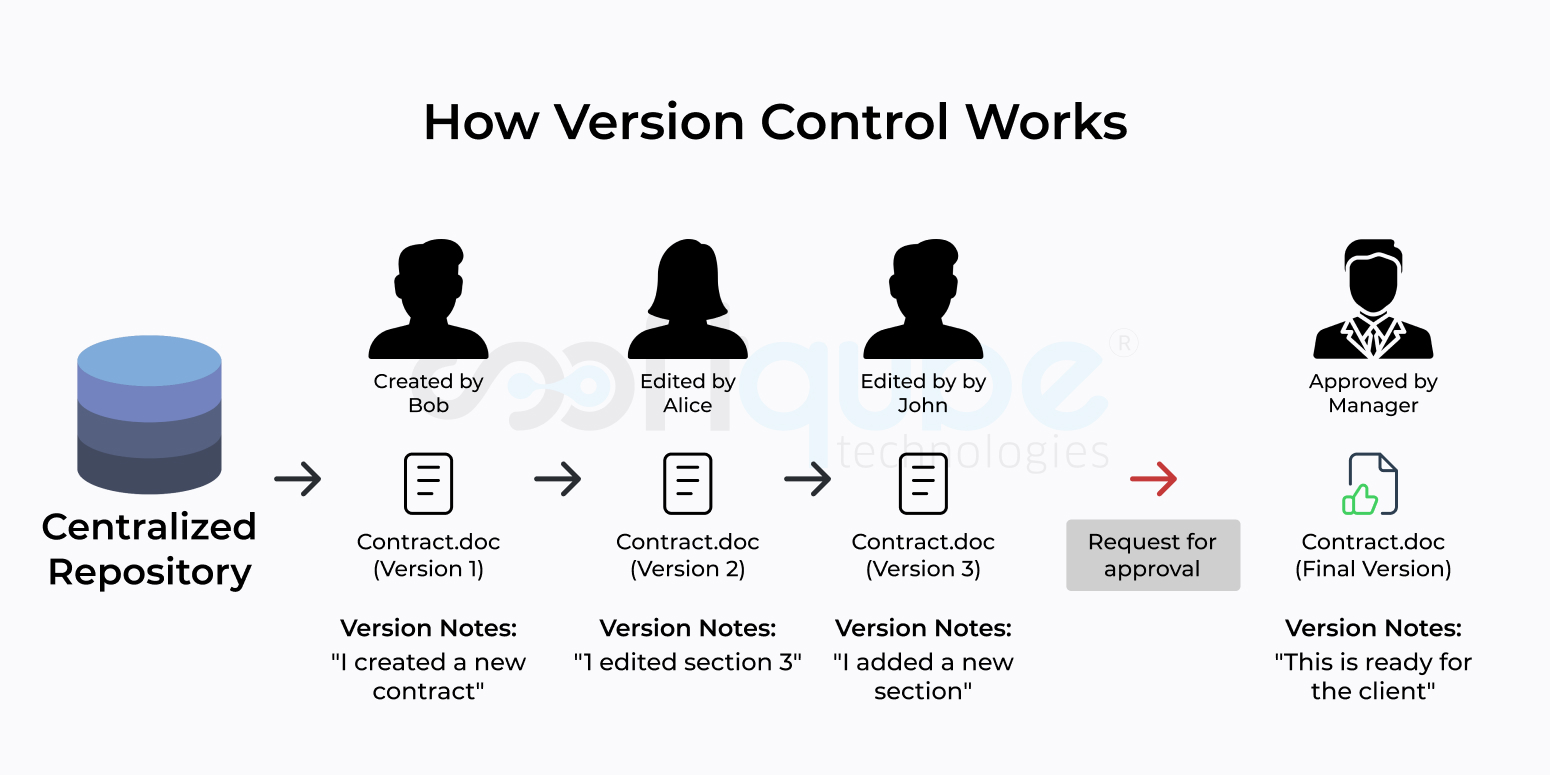
The backbone of the futuristic DevOps ecosystem is CI-CD Pipeline implementation belonging to the Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment Software. The pipeline has a great influence on the software and applications by way of providing periodic and steadfast updates to them In addition, it provides an agile and collaborative workflow for the entire DevOps squad.
With the help of test automation, CI/CD pipeline identifies the estimated issues way before anyone can find out, push codes the changes to different environments, and provides applications to the production environments. From performance to API and security, test automation analyses and assesses anything. This further becomes the most crucial source for pipeline quality control.
Know the differences between CI, CD, and CD?
Continuous Integration
It is a software development method where the team members can unite together for a minimum of one time a day. Here, an automated build to search tool assesses every small unification or integration with an aim to find out the errors.
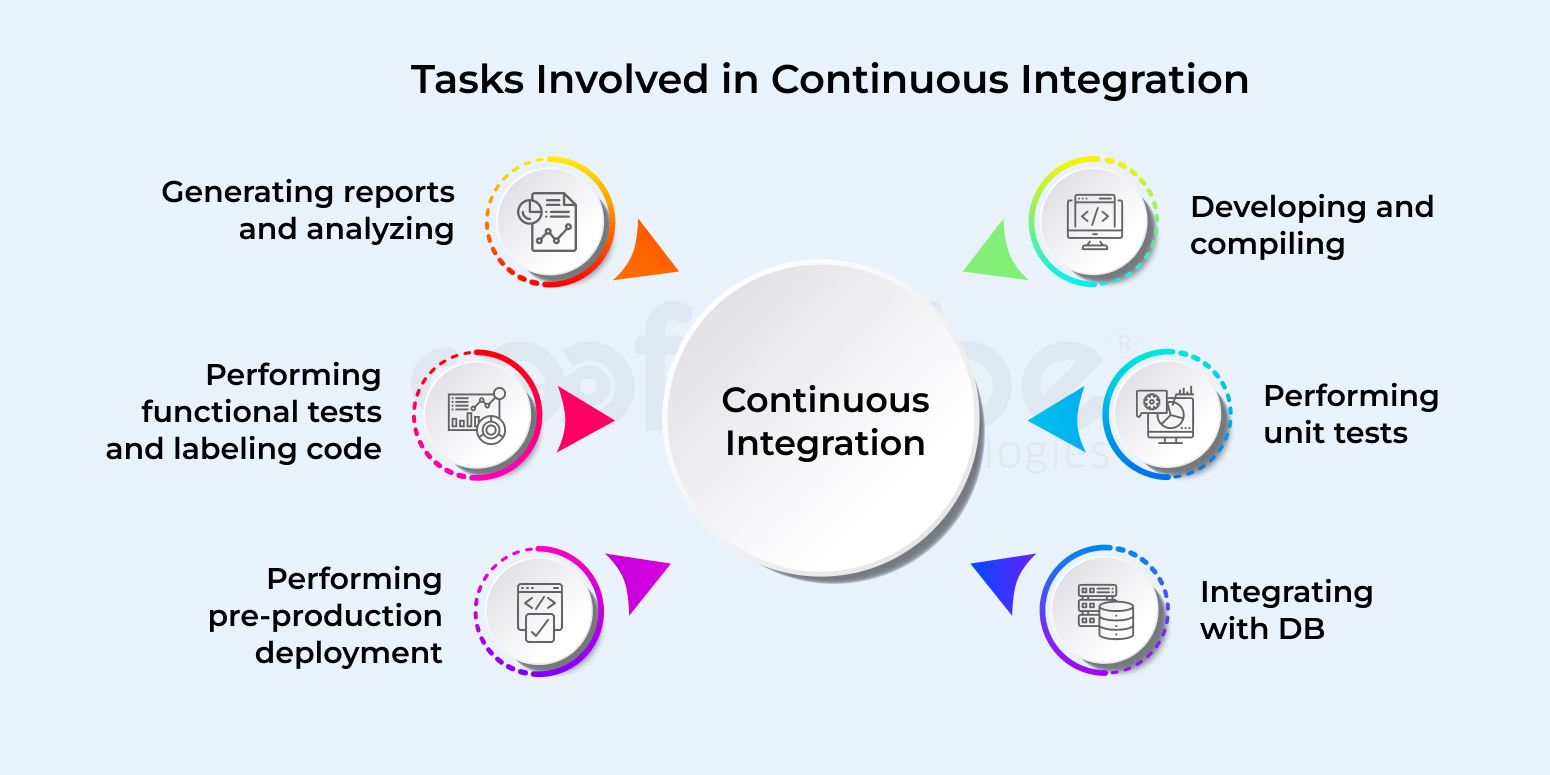
Pros of CI (Continuous Integration)
- Automated monitoring of codebase, code coverage metrics, and code quality health
- Low maintenance expenditure and keeps down the technical debts
- Developers get a boost to enhance code quality with publicly-visible code quality metrics
- A candid overview of the present scenario of development efforts is known with automated end-to-end acceptance tests.
- Lesser risks over a period of time due to the quick feedback mechanism
- Tools created to facilitate trace and fix integration and regression issues quickly so as to avoid more bugs and ensure fast delivery
- Enables simplification of delivery and amplifies it through automation of deployment process. With this in place, the testers and end-users get quick access to the software.
Continuous Delivery
CD is a process of software engineering whereby a group of developers creates software within a short time span to ensure its quick delivery at a given time.
Pros of CD (Continuous Delivery)
- Lesser Risks: The aim of CD is to develop effortless software deployments and make low-risk events that can be performed whenever demanded
- Quicker Time to Market: Every integration and test/fix phase of the traditional phased software delivery lifecycle takes time more than weeks and months.
- Decrease in Costs: The growth of any software product or service occurs only after a considerable time span of usage and the experience of its results
- Sound Products: CD is inexpensive in terms of working within small batches. You can take feedback from its users through the entire delivery lifecycle depending on the working software.
- Joyful teams: When the research gets a fair review from counterparts and peers, you improve with a continuous delivery that is less painful and decreases team burnout.
Continuous Deployment
This is another process of software engineering delivering functionalities with automatic deployment. The testers get support for validating the codebase changes and ensuring their correctability and stability.
CD also can be considered as a step ahead of Continuous delivery wherein each change in the source code is deployed to production automatically with no approval needed from a developer.
Pros of CD (Continuous Deployment)
- Software release process automation: CD allows your developers’ group to automatically create, test, and make code changes for production release in order to deliver the software with speed and effectiveness.
- Accelerates Developer Productivity: Your team gains higher productivity by making it more independent from doing manual tasks and promoting behavior that ensures error reduction and lesser bugs deployed to the customers
- Traces and Addresses bugs quickly: Your team gets enabled to track and address the bugs quite before they become a big problem leading to frequent and aggressive testing. CD also allows flexibility to execute extra tests on your code with an intention to automate the entire process.
- Quick Delivery of Updates: CD facilitates the team to provide regular updates to the customers with speed and frequency. With proper implementation, the CD can give you a deployment-ready build artifact gone through a rigorous testing process.
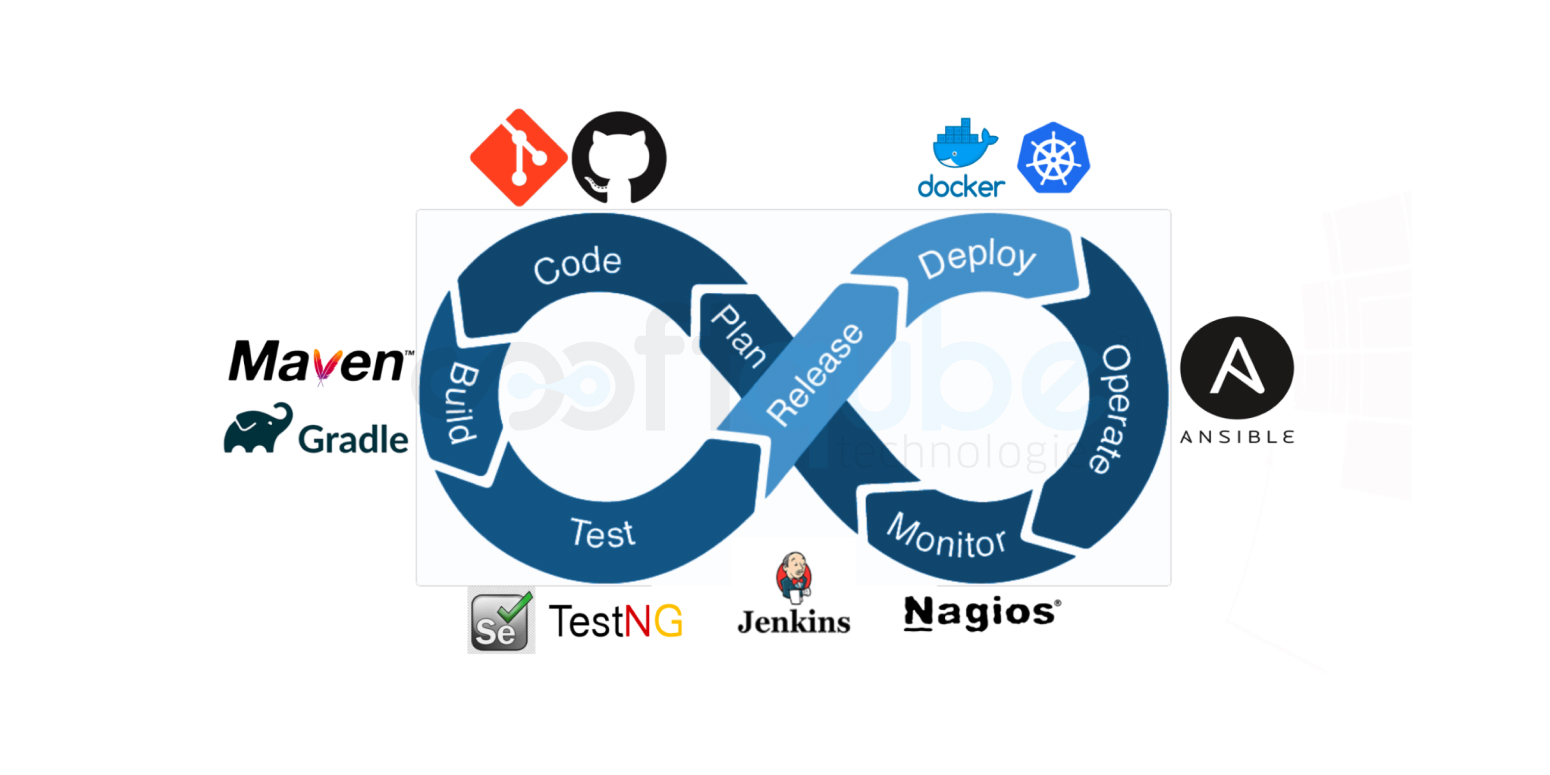
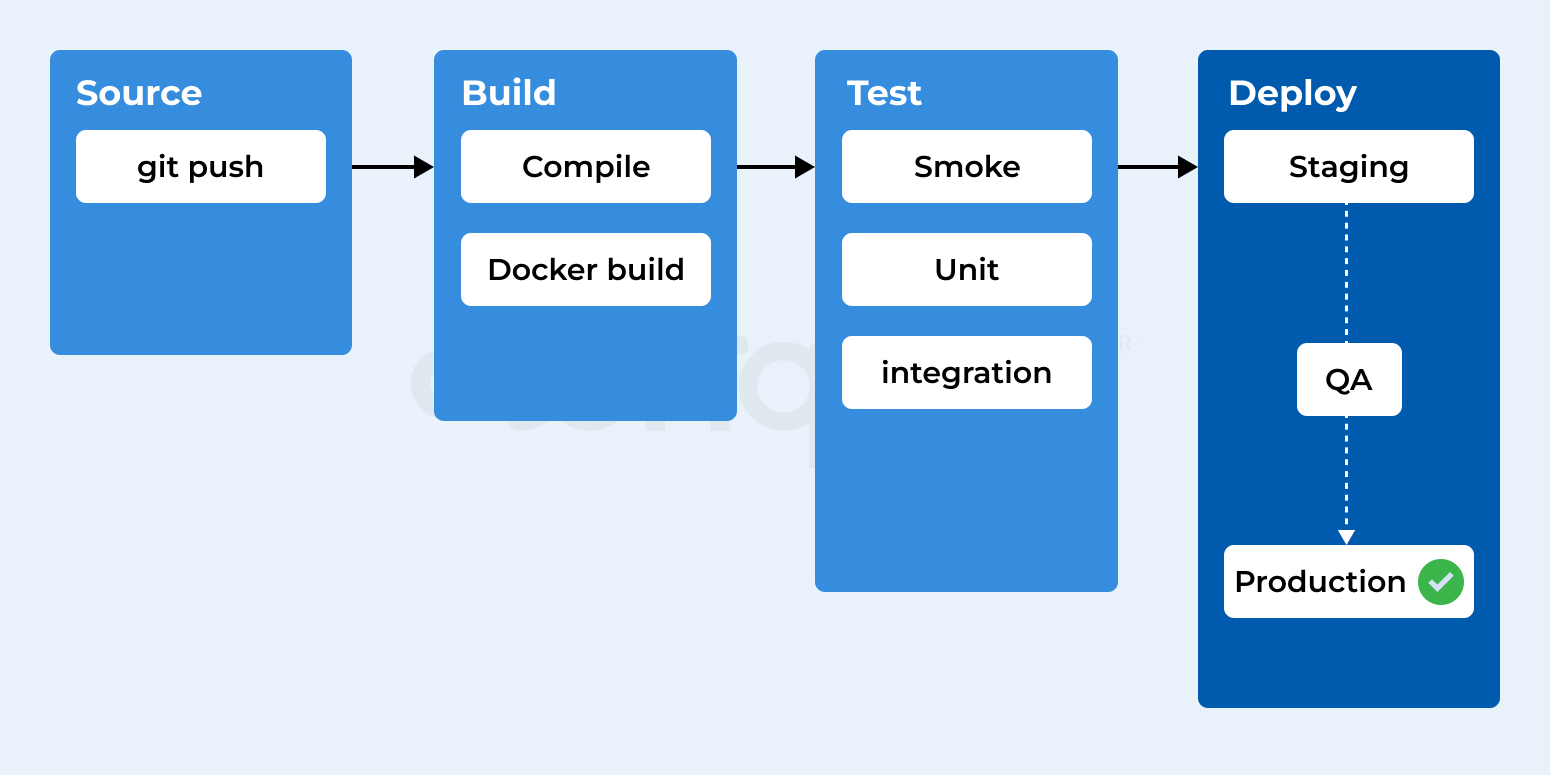
Stages of CI/CD Pipeline
The importance of CI/CD pipeline dwells in the steps with runnable specifications. These steps are required to be performed to ensure the delivery of the new version of the software product. Generally, CI/CD version comprises following stages:
Some common CI/CD tools
CI/CD tools assist the team to automate the development, testing, and deployment of the software. There are certain tools handling the integration (CI) side, while some handle the development and deployment (CD). The others develop a specialization in continuous testing or related functions.
The most popular open-source tool for CI/CD is the Automation Server Jenkins. Jenkins is created with an aim to manage and control everything beginning from a simple CI server to a fully operational CD hub
The fundamental tools of DevOps mostly become a part of CI/CD process. For example Configuration Automation (like Chef, Ansible, and Puppet), Container Orchestration (such as Kubernetes), and Container Runtimes (like Docker, CRI-O, and RKT). All this also shows up in several CI/CD workflows.
Conclusion
During the usage of CI/CD, the code quality gets augmented and there is a quick delivery of software updates. All this happens with great assurance of no breaking changes. For every release, its influence is definitely correlated with data starting from production and going towards operations.