DevOps Tool: SCM (Source Code Management)
For any IT company, Source code management (SCM) becomes the fundamental element of a development project. In this phase, the development teams work and evolve with collaboration.
SCM ensures you get what you want from what you have. It doesn’t start with the production but also is involved in the development phase. SCM offers the team various benefits that serve as safety nets. SCM can be undertaken either formally or rigidly. Also, it can be performed in several other informal ways.
Purpose
The core purpose of SCM is enumerated below:
- To track the modifications to a source code repository
- To keep a check on the running history of changes to a codebase.
- To facilitate in resolving conflicts that arise during the merging updates from varied contributors
- Synonymous with version control
SCM contains several benefits listed below
- Team Work and Collaboration
- Version history
- Code Backup
- Create release notes
With SCM implementation, you will always follow the best practices that reflect the reason for its creation.
- Frequent commitment
- Make sure the user uses the latest version
- Always make detailed notes
- Before making the commitment – always review
- Check with the branch team consent
SCM Tools:
Version Control:
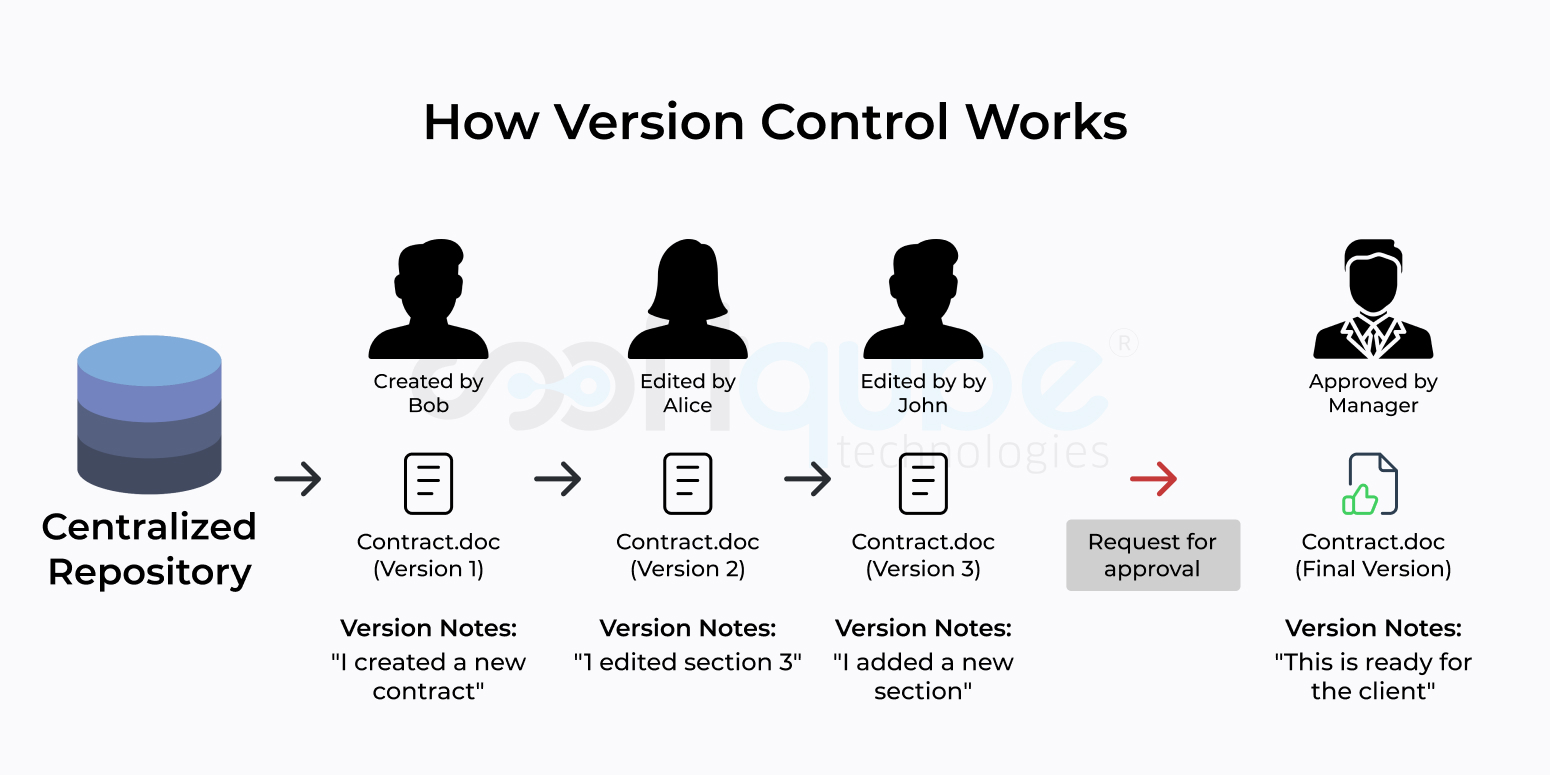
Version control system tracks and controls the location changes that comprise a particular set of files remaining for a longer duration. The VCS system is also utilized for the storage of image and layout versions.
Benefits of Version Control System
- Version storage
- Previous versions storage
- Collaboration
- Back up Facility
- Situation Analysis
What is Git?
Git must be used for tracking all the changes that take place in various sets of your files. Git is that version control system that we can use for coordinating the work of the programmers. In the majority of cases, it is used for source code management in software development. The action takes place with various goals attached to it like data integration, supportive distribution, non-liner workflows, etc.
We can use vcs for:
- Storage
- Sharing
- Differentiating
- Tracking changes
- Rolling back
- Removing the fear of making changes
- Avoiding computer glitches
- Conserving old states
Basic commands of Git:
$ git init
Git repository initialization in a local folder.
$ git status
Status check of git repository
$ git add .
changes added to the working directory and staging area
$ git commit -m “message”
takes the snapshot of the current project’s staged changes.
$ git remote add <URL>
local repository connection to remote git repository.
$ git push
content upload of local repository to a remote repository.
$ git checkout <branch>
Specific branch checkout as a working directory.
$ git diff <ver1> <ver2>
Version specific comparison of git repository.
$ git clone <URL>
cloning of remote repository to local folder.
$ git pull
remote git repository merging with changes to local git repository.
Few Advanced commands of Git:
Merging vs. Rebasing
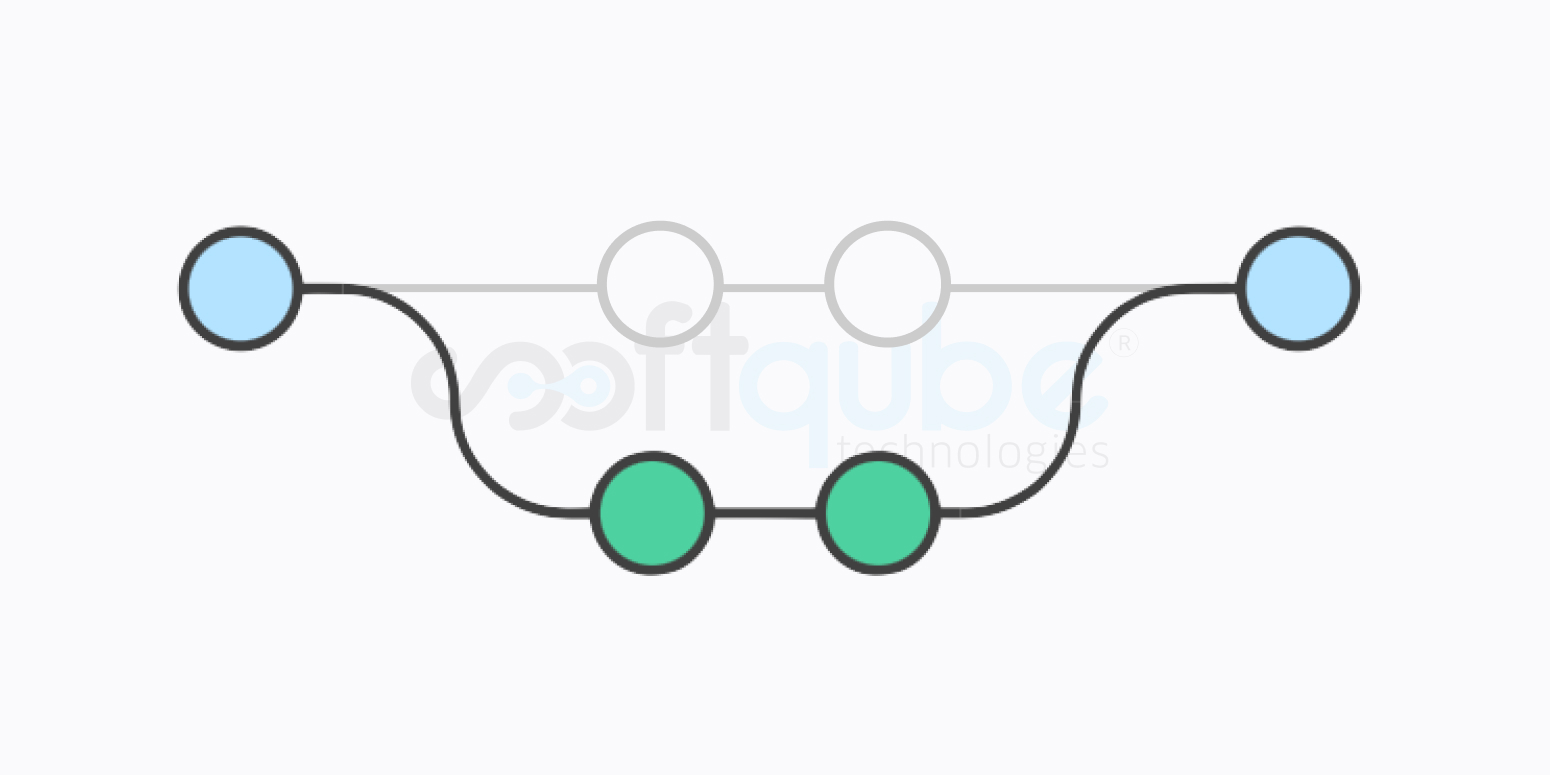
When you want to work with the divergent history, select Git. The git merge and git rebase commands provide different ways for commits integration from various branches. Also, know that both the options come with their own advantages.
Resetting, Checking Out, and Reverting
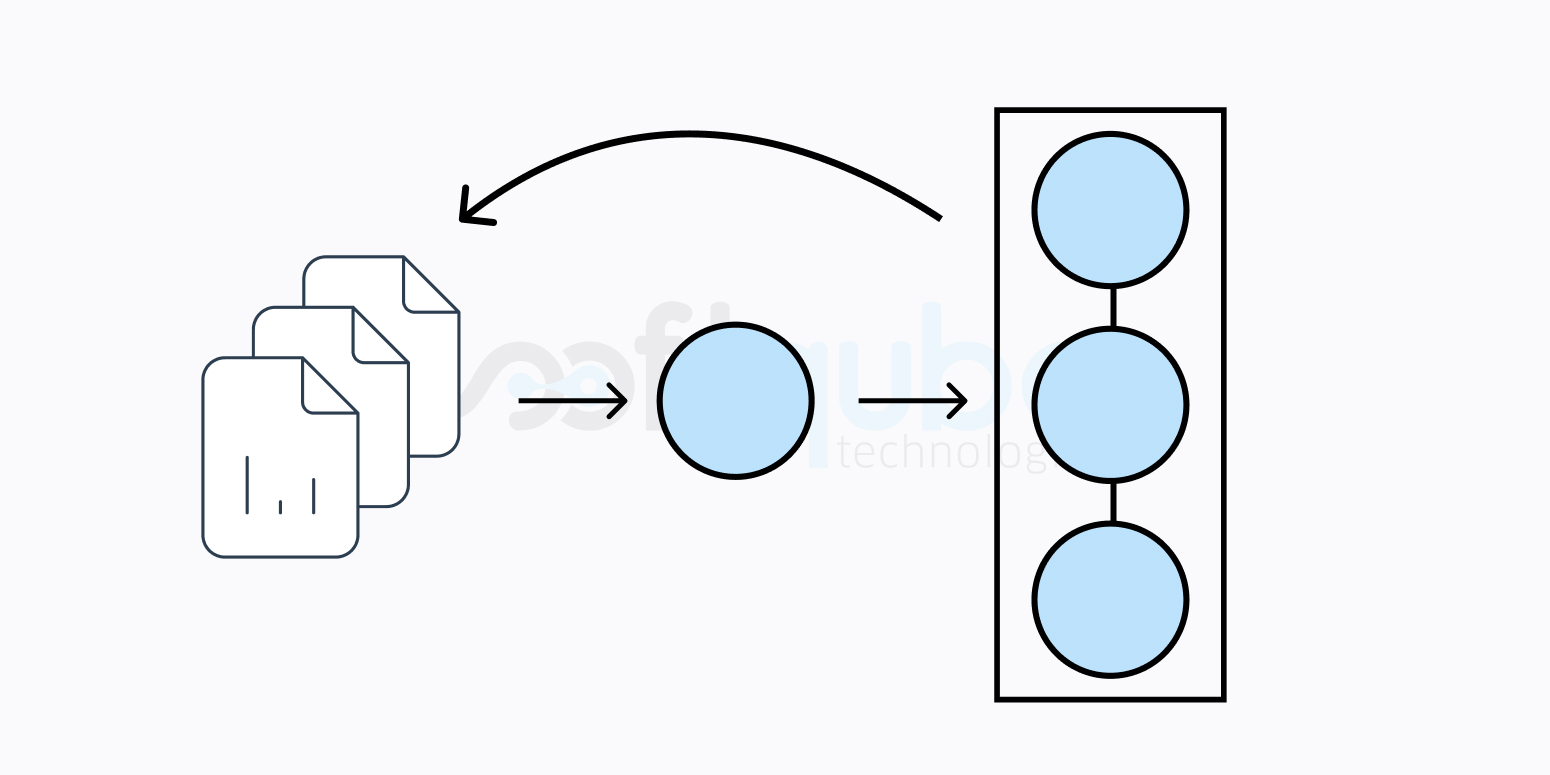
The Git commands undo particular changes in your repository via git reset, git checkout, and git revert commands. However, they create a varied impact at different places with different combinations of the working directory, commit history, and stages snapshot.
Advanced Git Log
Your project history becomes useful because of the git log command. Like most aspiring Git users, there is no doubt if you are found scratching the surface of what is all possible with git log.
Git Hooks
Hooks are special tools of choice that you can use for performing custom actions during the happening of certain events. They always let you normalize commit messages, notify continuous integration systems, automate testing suites, and do much more.
Refs and the Reflog
Refs are the internal way of Git and refers to a commit. Since now you must be already familiar with lots of categories of refs that also include commit hashes and branch names. However, there are so many other types of refs that are virtually used by Git command in some form or another.
Conclusion:
Software configuration management comprises several sets of policies, procedures, and tools to lead to a successful development process. Git is a VCS that tracks the changes in computer files. And GitHub offers an online git repository hosting service with a web interface to upload the files. Various operations of the branching are – create, merge, delete, and checkout a branch. The entire system is impressive because it facilitates the team to work in coordination so that they can perform the changes in an orderly fashion from the idea generation to production to retirement. This can surely avoid chaotic and ambiguous situations in the future.