Table of Contents
Ed Harris was one of our clients with a creative and innovative idea that would serve the purpose of solving a core market problem. He went on to create a robust software application built up and backed with strong foundations with the help of top-notch software development experts. We helped him build world-class software that was embedded with the right design decisions, a deeper understanding of the product by the design experts and architects, and easy comprehensive codes.
To build a classic software model needs a lot of research on everything about software architecture. It is not just about the definitions and user interface designs. There is much more to that. Head on to the below list of topics that we shall cover for you and help you understand all the aspects related to software architecture.
What is Software Architecture?

Basically, software architecture is a blueprint for the development team to understand the user expectations and undergo a deeper analysis on the system design before applying iterations throughout the development cycle.
A constantly evolving process with an integrated set of pattern-oriented software architecture and technical decisions is called Software Architecture. It simply exemplifies transversal attributes like performance, scalability, quality, manageability, maintainability, and usability. It is inevitable to execute an indepth analysis before you begin writing your first line of code in order to get an effective development process.
When all the developers unite from the very beginning to develop robust software it guarantees a structured, consistent, and scalable development. Well-organized software architecture defines simple maintenance of internal quality and leads to continuous software improvement.
The Five Principles of Software Architecture
An ideal software architecture plan adheres to the five principles abbreviated as S.O.L.I.D design principles. They perfectly resonate with the software development objectives and with the software architecture. A correct application of these principles ensures avoidance of product strategy mistakes in the future.
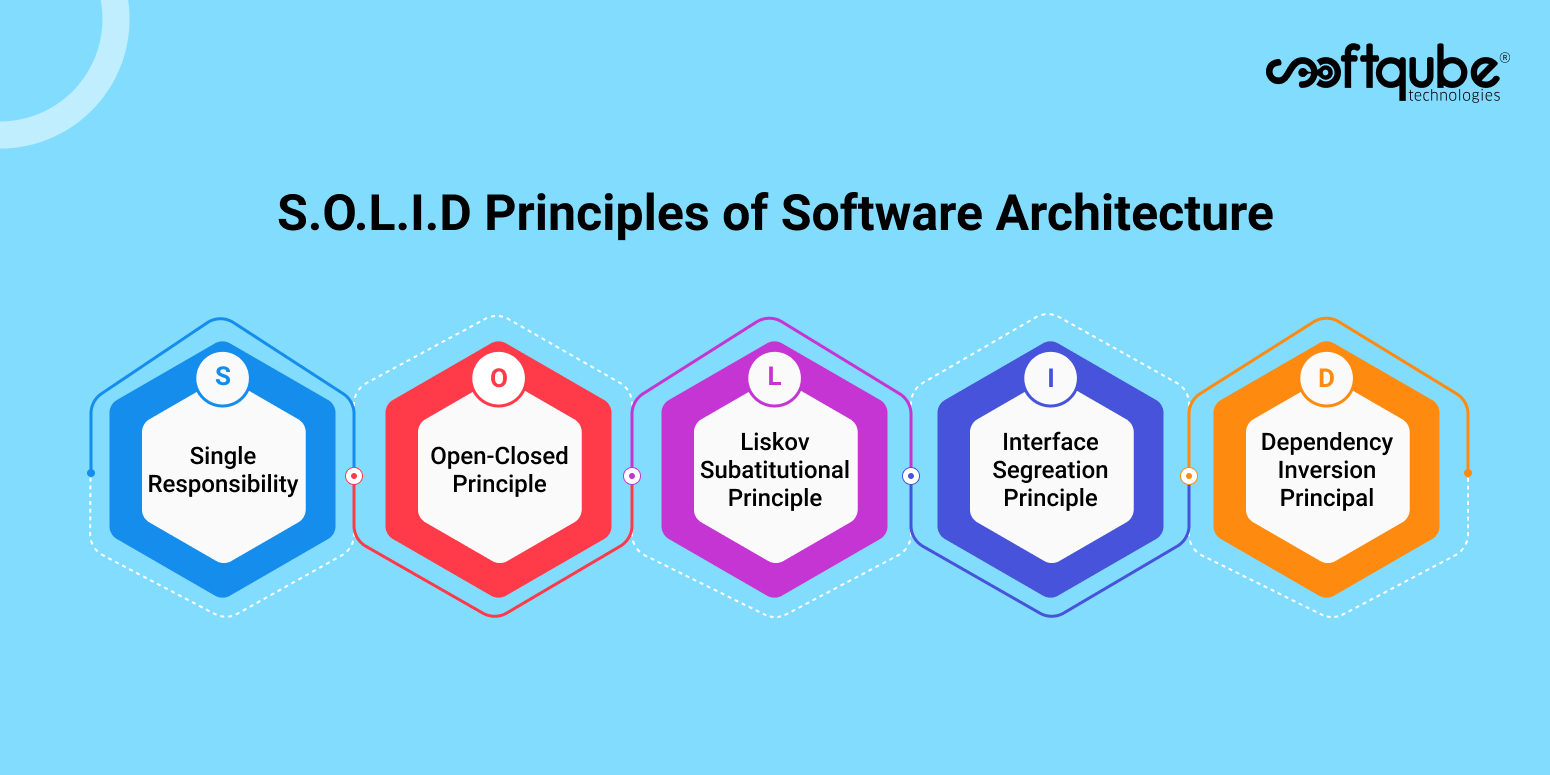
1. Single Responsibility Principle
All these services in the microservice architecture must be designed to comply with the single most objective. They should work with a unique responsibility and should become the core reason behind the application of the change.
2. Open-Closed Principle
Must be easy to expand the functionality of independent software modules. The specific service expandability should not impact the original behavior of the software.
3. Liskov Substitution Principle
There should be communication between any two independent services whenever required through API calls. The two services with the same contract should be capable to act as a substitute between each other, again without disturbing the overall system.
4. Interface Segregation Principle
You need to divide the software into microservices in such a manner that there are zero redundancies present. The smaller modules should be combined meagerly to satisfy the client’s needs along with minimizing the anti-patterns in the code.
5. Dependency Inversion Principle
High-level modules must not be dependent on low-lower-level modules. Rather both of them should lean on abstractions. With the same principle, the abstractions should rely on details, while the vice-versa holds.
What Takes To Have A Good Software Architecture
Some of the finest quality attributes are needed to ensure a good software architecture in making. Let us know which are those.
- Functionality: The level of performance of the software against its intended purpose.
- Reliability: The ability of the product to offer desired functionality under the given conditions.
- Usability: To what extent the software product can be used with ease.
- Performance: Estimation by considering processing speed, response time, resource utilization, throughput, and productivity.
- Supportability: The ease with which programming developers can transfer software from one platform onto the next, without any or with minimal changes.
- Self-Reliance: The ability of the independent services to perform optimally even if one of them suffers a downtime.
Factors Defining a Good Software Architecture
If you need an ideal software product architecture what is needed is the least amount of cruft – It is the difference between the current code and what should be the actual code. Higher the cruft, poorer is the software design and architecture. We shall know about the four factors responsible for helping out to trim down the cruft in the entire development process.
Architecture Structure
The type of architectural design defines its structure. For eg. Microservices architecture or even a layered or even a layered architecture. These design decisions depend upon the software development team.
Architecture Characteristics
The success of any product in question is all dependent on the good software architecture characteristic. The characteristics can be generalized in nature and need not necessarily detail out a particular functionality of the software system.
Architecture Decisions
The phase is meant to lay out standards that you need to follow while converting ideas into products. To cut it short, the decisions define the how the development team works on the allocated tasks.
Design Principles
The design principles and architectural decisions both almost come from the same land. The line of differences is only during designing software architecture. Various guidelines are laid out and need to be followed as compared to the stringent instructions of the architecture decisions. The UX design process gets the right navigation through these guidelines.
Most Popular Software Architecture Patterns
An array of design decisions that keeps on repeating and has well-defined properties that can be reused with a class-apart set of architectures is called a software architecture pattern. These patterns provide a great way to capture proven good design architectures in practice. The building of architecture includes selecting, combining patterns, and tailoring.
There are five major types of software architecture patterns. Read on below to find out which they are.
1. Layered Architecture Pattern
The layered software architecture works upon a tiered approach under which one layer offers services to the higher layer. It is amongst the commonly used patterns throughout the software industry as it is simple to develop and maintain. In the layered architecture pattern, all the components are interconnected and don’t depend on each other. MVC (Model-view-controller) pattern is a common example of a layered architecture pattern that works upon a three-layer approach.
When to choose a layered architecture pattern?
- You have less time and developers and need to design an app quickly
- Apps that specifically need strict maintainability and testability standards
- Business apps that require to embrace traditional IT structures
2. Event-driven Architecture Pattern
Unlike the layered software architecture pattern, an event-driven architecture pattern is a modern approach that centers around data that describes “events.” This pattern enables the app modules to act on defined events when they occur. It includes single-purpose event processing components that listen to events and process them asynchronously. These patterns comprise two categories- broker topology and mediator topology.
When to choose an event-driven architecture pattern?
- Develop complex apps that demand seamless data flow
- User interfaces
- For apps having asynchronous data flow systems
3. Microkernel Architecture Pattern
Microkernel architectural pattern, also known as a plug-in architectural pattern, is utilized when software teams build systems with interchangeable components. The pattern is ideal for applications that require sufficient flexibility to adapt to the evolving system requirements. It is divided into two segments:
Minimal functional core: The system includes general business logic with no custom code for complex conditional processes.
Extended functionalities: The extended functionalities, i.e., plugins are a group of independent components supporting the core by offering specialized processing additional features through custom code.
When to choose a microkernel architecture pattern?
- Workflow applications
- Apps that need separation between low-level functionalities and higher-level functionalities
- Task & job scheduling applications
- Developing enterprise apps as this pattern offers scalability, extensibility, and portability
4. Microservices Architecture Pattern
The microservices architecture pattern follows the process of developing small independent apps that communicate with each other so that the entire system works seamlessly. The pattern enables developers to deploy the apps independently and further offer a high degree of application and component decoupling within the app. Since microservices communicate with each other, you must ensure that the messages sent across them persist in being backward-compatible.
When to choose a microservices architecture pattern?
- Corporate data centers with well-defined boundaries
- Apps with immense and rapidly growing data systems
- Developing new businesses and web applications quickly
- Re-writing monolithic applications to a more sustainable pattern
- Websites with small components
5. Space-based Architecture Pattern
Space-based architecture pattern is amongst the popular software architecture patterns that address the scalability and concurrency issues and is helpful in the case of apps having variable and unpredictable concurrent user volumes. The pattern is based on the concept of tuple space.
According to Wikipedia, A tuple space is an implementation of the associative memory paradigm for parallel/distributed computing. It provides a repository of tuples that can be accessed concurrently.
The processing unit component includes web-based components and backend business logic. Smaller web apps can be deployed in a single unit, while the larger ones are fragmented into multiple processing units. The virtualized-middleware component includes elements responsible for data synchronization and controlling handle requests. There is no central database throughout the space-based architecture pattern.
When to choose a space-based architecture pattern?
- eCommerce or social website development
- High-volume data like clickstreams and user logs
- Apps addressing scalability and concurrency issues
Conclusion
An ideal software architecture embedded with all necessary components of creativity and innovation can help maintain quality software throughout the life span. It can also help in segregation software into microservices that will ensure effortless management activities. However, the truth is nobody can get it right at the very time.
The best of the software product development projects will face cruft. And during these situations, a team of agile-driven expert professionals can trace these mistakes and get rid of them sooner or later. Good software architecture can save a lot of developers’ time and can prove to be profitable for the business. Make it possible by signing in your next software architecture development project with our Softqube experts who shall help you design software with a robust and scalable architecture.

